WNY Farms Company instrumental in turning swampy marsh into mucklands, Part 1
By Catherine Cooper, Orleans County Historian
Illuminating Orleans, Vol. 2, No. 16

“Wall Street goes a-Farming” was the title of an article in Popular Science Monthly, Spring 1917 which described the gigantic Oak Orchard Farm:
“an admirable example of what a great farm can be when conducted under the precise and systematic management of ‘Big Business.’”
A mere four years prior, the “great farm” was an overgrown swampy marsh, reclaimed by an ambitious drainage project. The “Wall Street” reference in the article’s title was to the Western New York Farms Company, with an address at 49 Wall Street, New York, NY which had been incorporated on March 9, 1911. The directors were Andrew A. Smith, 40 South Washington Square, NY; H.R. Tobey, 109 West 45th St., NY; and Morris K. Parker, New Cannan, Conn.
By 1913, the Farms Company had acquired large tracts of land in Barre and Clarendon.
The initial impetus for draining the swamp was health, not agriculture. Malaria had long been associated with swampy land. Drainage of the swamp for health reasons was first recommended by the State Supreme Court in 1903. In 1904, Commissioners Avery Danolds of Shelby, John Crowley of Medina and Joseph W. Holmes of Batavia recommended draining almost 25,000 acres of swamp. They estimated the cost of surveys and preliminary work at $5,000. This would be assessed to the six towns involved, the costs to be reimbursed by the property owners.
This proposal languished but was presented again in 1910, as a “public necessity” according to the Medina Daily Journal, August 15, 1910. Meanwhile, the agricultural value of the drained land attracted attention when several experts attested to its fertility and potential. Plans were finalized in 1910 when it was agreed that the project should continue and be paid for by the owners of the land which benefited by it. The work began in 1913.
There had been some local resistance to the project. A letter from a Clarendon Taxpayer published in the Democrat and Chronicle and the Orleans Republican on January 12, 1912, outlined many concerns regarding this “scheme of public exploitation for private gain…under the guise of public health.” The Clarendon Taxpayer asked:
• Who would be responsible for maintaining the ditch?
• What effect the massive drainage would have on the remaining timber?
• What effect would the winds and the absence of moisture have on the climate, the orchards, and the crops of those who lived north and east of the area?
• What effect would the drainage have on wells? If residents had to drill deeper, they ran the risk of encountering sulphur or salt which would render the well unusable?
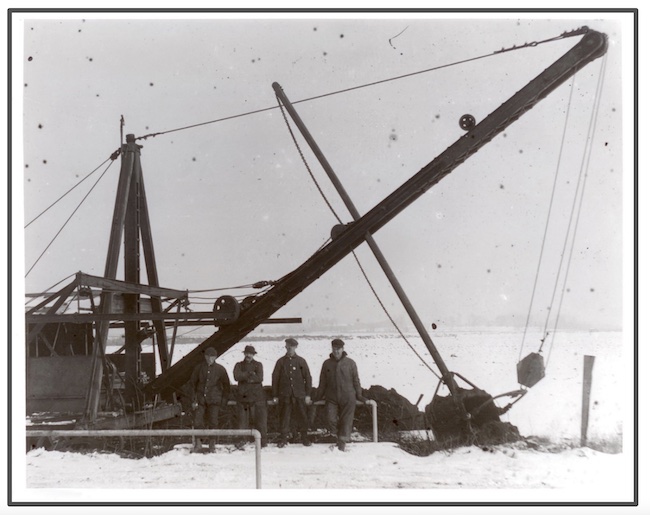
The project proceeded on a large scale. It comprised some 9,000 acres in the Orleans County towns of Barre and Clarendon, as well as in Elba and Byron in Genesee County. In 1913, workmen operating huge dredging machines dug 21 miles of main canals and 20 miles of laterals located about 2,000 feet apart. To accommodate the runoff, a channel through the Oak Orchard Creek was enlarged and straightened. Sixty Adirondack lumberjacks felled timber. Underbrush was burned. Crews operating plows, harrows, cultivators, and seeders prepared the soil. The first crop of vegetables was harvested in 1915.
All of this activity was overseen by the Western New York Farms Company’s Double O Ranch, a large facility in Elba, which had its own machine and maintenance shops, evaporator, cannery, and accommodation for workers, some four thousand in all.
The Farms Co. began leasing sections of land to growers in 1916 at the rate of $50 per acre for the first year. This included assistance and machinery. Subsequently, the rent was $35 an acre but no assistance was provided. It also offered land for sale, in 5 acre lots, at $300 per acre. The terms were one quarter to be paid in cash and the remainder in four equal annual installments.
The company sold its holdings in 1927, at $573.50 per muck acre, with an annual maintenance fee of $10 per acre. Priority was given to existing tenants and mortgages were available at 6%.
The Western New York Farms Company “Wall Street” approach to agriculture introduced agribusiness methods to Orleans County – mechanization, large scale production, scientific approach, efficient management. Muck landowners formed the Genesee-Orleans Vegetable Growers Co-op Association in 1921. This group assisted with marketing, encouraged development, and espoused advocacy. The “Wall Street” legacy continued.
For additional information see: www.albionalumni.org/chevrons/alb/muck.html.